Optical Transceivers-The Ultimate Guide for Beginners and Experts
In today’s world where the Internet and artificial intelligence are developing rapidly, optical modules, as a core network communication equipment, play an increasingly important role. Today’s article will provide a comprehensive introduction to the definition, function, design, type, price, market and application, and famous industry manufacturers of optical modules. Whether you are a newcomer to the industry or an expert, this article is suitable for you.
What is an Optical Transceiver?
An optical module is an electronic device that converts optical signals and electrical signals into each other.
What are the roles of Optical Transceivers?
As a transmission medium between network devices, the optical module is a necessary hardware device for long-distance communication. Its function is to convert electrical signals into optical signals at the transmitting end. The optical signals are sent to the receiving end through optical fibers. The optical module at the receiving end converts the optical signals into electrical signals. In short, the role of the optical module is to send and receive data.
Optical Transceiver Design
Optical modules are designed to be small and compact, making them easy to install in any network equipment such as switches. The following will take you to understand how an optical module is designed, starting from the basic structure and main technical parameters of the optical module.
Structure of An Optical Transceiver
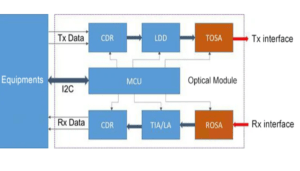
An optical module is mainly composed of optical transmitting components, optical receiver components, functional circuits and optical (electrical) interfaces.
At the transmitting end, the original electrical signal is processed by the driver chip, and then the semiconductor laser (LD) or light-emitting diode(LED) is driven and emits a modulated light signal.
At the receiving end, after the optical signal comes in, it is converted into an electrical signal by the light detection diode, and the electrical signal is output after passing through the preamplifier.
The above are the basic design principles of optical modules.
The Main Parameters of Optical Transceiver
The main technical parameters of the optical module are as follows:
Packaging type: With the continuous advancement of economy and technology, the packaging types of optical modules are also constantly enriched and developed according to market needs. The main packaging types currently on the market are GBIC, SFP, XFP, QSFP+, OSFP, QSFP28, QSFP- DD, COBO, etc.
Transmission distance: Optical fibers have certain side effects such as loss during the transmission of optical signals. The transmission distances of optical signals emitted by different types of light sources are different. Transmission distance can be roughly divided into short distance (within 2km), medium distance (2-20km) and long distance (30km/40km/80km, etc.).
Center wavelength: The wavelength when the optical module is working is actually a range. It is called the center wavelength for the convenience of description. The unit of central wavelength is nm, and there are currently three main types:
- 850nm (multi-mode MM), low cost but short transmission distance, generally only 500m;
- 1310nm (single-mode SM), which has large loss during transmission but small dispersion, and is generally used for transmission within 40km;
- 1550nm (single-mode SM), with small loss but large dispersion during transmission, is generally used for long-distance transmission of more than 40km, and can directly transmit up to 120km without relay.
In addition to the above three main center wavelengths, there are also 1270nm-1610nm of the CWDM series (spacing 20nm) and 1528nm-1623nm of the DWDM series (spacing 0.8nm or 0.4nm).
Transmission rate: The transmission rate refers to the number of bits of data transmitted per second, and the unit is bps. The transmission rate has developed from Gigabit per second in the 1990s to 800G and 1.6T today. Of course, there are also 0.5M, 2G,10G, 25G, 40G, 100G,200g,400g and other rates in between.
The above four main technical parameters are the main concerns of those engaged in the optical module industry. Of course, you will also see other relevant technical parameters in the detailed specifications or promotional materials of each manufacturer, such as output optical power, acceptance sensitivity, laser type, optical module interface type, ambient temperature, service life, extinction ratio, and optical saturation , loss and dispersion, maximum power consumption, etc., I will write a special article to introduce it in detail later.
Types of Optical Transceivers
There are many classification methods for optical modules based on different standards. For example, the classification standards include packaging method, transmission rate, transmission distance, transmission method, central wavelength, fiber type, interface type, applicable temperature range, manufacturer, application field, etc. Currently, it is common on the market to classify optical modules based on packaging methods and transmission rates.
Packaging method: According to different packaging methods, optical modules can be divided into six types: SFP/SFP+/SFP28/QSFP+/QSFP28/QSFP-DD. Each package has its own characteristics.
The main features of the SFP series optical modules are small size, hot-swappable support, and transmission rates ranging from 1.25G to 1.6T.
Transmission rate: According to different transmission rates, optical modules are generally divided into 0.5M, 1.25G, 2G, 10G, 16G, 25G, 32G, 40G, 100G, 200G, 400G, 800G, 1.6T etc.
Optical Transceivers Prices and Market
Optical module market
After 25 years of development, the optical module industry has roughly gone through three stages. With the rise of the Internet in the 1990s, optical modules also emerged; in the first decade of the 21st century, the optical module industry has achieved initial development; in 2020 In the future, thanks to the rapid development of artificial intelligence, 5G, and the Internet of Things, the development of the optical module industry has also entered the fast lane. It is expected that the global optical module industry will reach about 16 billion US dollars in 2024.
Optical module price
In the past ten years, with the rapid expansion of the optical module market, the average market price of optical modules has also dropped from US$50/unit in 2016 to US$15/unit in 2023. Specific to the price of different models, the unit price ranges from about 2 US dollars for 1G to about 1,000 US dollars for 800G.
Optical Transceiver Application
The application scenarios of optical modules are mainly divided into five categories, namely:
Data center interconnection: With the rise of big data, VR, Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence, original data centers can no longer meet such a large amount of data processing needs. Coupled with space and energy supply constraints, most of the expanded data centers have to be located offsite. The interconnection between the new data center and the original data center requires higher transmission rate, lower power consumption, and smaller equipment. Therefore, a core device that determines whether these requirements can be realized is the optical module.
In the data center application scenario, optical modules are mainly used in servers, top-of-rack switches, core switches and other equipment.
Mobile communication base station: With the rapid development of smart phones, people are gradually understanding the concept of mobile communication base station. A mobile communication base station refers to a radio station that transmits information to mobile phone terminals through a mobile communication switching center within a certain radio coverage area. The interconnection between key equipment in mobile communication base stations also requires optical modules.
Passive wavelength division system: Passive wavelength division system is mainly composed of colored optical modules and OTM passive devices. Passive wavelength division technology refers to coupling optical signals of different wavelengths with a series of information into a bundle through WDM technology, and transmitting them in an optical fiber to achieve transmission between services.
SAN/NSA storage network
With the rapid development of Internet technology, the types of data that various data systems need to process have also increased significantly. This situation has caused data systems to face great challenges.
The main functions of Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Network (SAN) are to separate data storage devices from the network and host systems. This not only It can manage information data and has good scalability, providing the most effective solution to the rapidly increasing amount of data.
SAN networks are mainly composed of servers, fiber channel switches, storage devices, optical modules, and fiber optic jumpers; NAS storage networks are mainly composed of NAS storage, switches, computers, optical modules, and fiber optic jumpers.
The optical modules used in the SAN network need to support the FC Fiber Channel protocol, and the optical modules used in the NAS storage network only need to comply with the Ethernet protocol.
5G network
Since the launch of 5G, the market demand for optical modules has increased significantly, mainly reflected in two aspects; first, the number of optical modules required by 5G will increase significantly. In addition to the previous demand for optical modules for fronthaul and backhaul, the 5G midhaul link A large number of optical modules are also required; another increase in demand is reflected in rate iteration. In the past, 4G mainly used 10G optical modules, while 5G fronthaul is expected to require tens of millions of 25G/50G optical modules, and backhaul requires 100G optical modules. The backhaul aggregation layer even requires 200G and 400G optical modules.
According to research data from relevant institutions, investment in China’s 5G network base stations is expected to reach US$700 billion, of which the demand for optical modules is approximately US$9 billion.
Top Optical Transceiver Manufacturer
Major global optical module manufacturers include:
- Coherent Corp. (US)
- INNOLIGHT (China)
- Accelink Technology Co. Ltd. (China)
- Cisco Systems, Inc. (US)
- Hisense Broadband, Inc. (China)
- Lumentum Operations LLC (US)
- Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. (Japan)
- Broadcom Inc. (US)
- Fujitsu Optical Components Limited (Japan)
- Intel Corporation (US)
- Molex (US)
- NeoPhotonics (US)
- Source Photonics (US)
Conclusions
As the core component of network communication systems, optical modules are bound to grow rapidly in the high-tech era led by artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing. Market demand will also drive the continuous update and advancement of optical module technology.
FAQS
How to clean optical transceivers?
First, we need to prepare an electric optical module cleaning pen or optical module cleaning rod, and anti-static gloves. Before handling the optical module, we must first wear anti-static gloves to prevent the optical module from being damaged by static electricity. After picking up the optical module, aim the electric cleaning pen at the optical fiber interface of the optical module, press the button and wait for about 1 second. The pen tip will automatically clean the port. Finally, pull out the pen tip to complete the cleaning of the optical module port.
For stubborn stains, you can repeat the above operation more often, or dip some alcohol into the tip of the pen before proceeding. If the cleaned optical module is not in use, cover it with a dust cap in time. If it is to be used, remember to wipe the fiber core on the optical fiber connector with fiber wiping paper to prevent the port of the optical module from receiving secondary contamination.
Can I use Single mode with a Multi mode transceiver?
Single-mode optical fiber and multi-mode optical modules cannot be mixed, and similarly, multi-mode optical fiber and single-mode optical modules cannot be mixed. Single-mode fiber is best used with single-mode optical modules, and multi-mode fiber is best used with multi-mode optical modules. Mixing single-mode and multi-mode cannot guarantee the effect, because multi-mode and single-mode converters must have corresponding wavelengths and optical transceiver functions to achieve photoelectric conversion.
What is the optical transceiver HS code?
The customs commodity code commonly used by Chinese companies for exporting optical modules is 8517706000. Different countries, regions and brands may use other commodity codes, but they are basically classified into the 8517 category.
Optical Transceiver Components and Block Diagram?
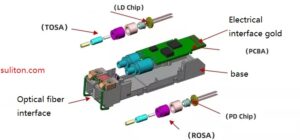
The optical module is mainly composed of three parts: housing, optical device and integrated circuit board.
Optical devices are the core components of optical modules. Different types of optical modules use different optical devices.
For ordinary optical modules, there are two optical devices, TOSA and ROSA, which have opposite effects.
TOSA refers to the light emitting component, whose main function is to convert electrical signals into optical signals.
ROSA refers to the optical receiving component, whose main function is to convert the optical signal transmitted from TOSA into an electrical signal.
The following block diagram illustrates the working principle of the optical module: