Difference between 400G ZR vs. Open ROADM vs. ZR+
Understanding 400ZR vs. Open ROADM vs. ZR+
Currently, there are three standards for 400G, 400G OSFP coherent technology, 400ZR, Open ROADM, and Open ZR+.
What Is 400G ZR?
400ZR is a standardized and interoperable coherent optical module interface launched by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF). Its target is coherent optical modules such as 400G CFP2, QSFP-DD, and OSFP used for Data Center Interconnect (DCI).
To meet this requirement, 400ZR requires that the power consumption of the module be lower than 15W, sacrificing certain transmission performance on the basis of the traditional coherent light transmission technology standards.
Only the 400GbE rate is defined on the client side. It adopts a solution combining Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) and DP-16QAM and uses CFEC (Convolutional Forward Error Correction). The transmission distance is 80 – 120 km.
What Is 400G Open ROADM?
Open ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add – Drop Multiplexer) is a significant development in the field of optical networking. Based on the success of the OIF, the standard Open ROADM MSA can support longer-distance transmission.
Open ROADM is specifically designed for OTN (Optical Transport Network) networks that need to support other protocols and increase the corresponding overhead bit ratio.
The Open ROADM MSA is mainly targeted at the ROADM network applications of telecom operators. On the terminal interface, 100G, 200G, and 400GbE rates as well as OTN are defined, with a transmission distance of 500 km. It adopts the openFEC (oFEC) algorithm.
What Is 400G ZR+?
400ZR and Open ROADM respectively define the types and performance characteristics of pluggable coherent optical modules for Data Center Interconnect and telecom optical transmission networks, but each also has certain limitations and drawbacks.
For example, 400ZR only supports the client-side interface of 400GbE, while Open ROADM only considers the network scenarios of telecom operators. Therefore, some mainstream manufacturers in the industry have combined the respective advantages of the OIF-400ZR and Open ROADM standards and launched another MSA standard, Open ZR+.
The application scope of the Open ZR+ MSA is broader, targeting metro areas, backbones, DCI, and telecom operators. It aims to achieve enhanced functions and improved performance in pluggable forms such as QSFP-DD and OSFP to support multi-vendor interoperability.
Open ZR+ not only maintains the simple Ethernet pure host interface of 400ZR but also adds support for multi-rate Ethernet and multiplexing functions for 100G, 200G, 300G, or 400G line interfaces. It also adopts the oFEC, thus having a higher dispersion tolerance and higher coding gain.
According to the Open ZR+ standard, 400G can achieve a transmission distance of 1,400 km, which is more than ten times the transmission distance of 400ZR.
Differences in 400ZR, Open ROADM, and ZR+
The comparison of the main performance indicators of the coherent optical modules defined by the three standards, namely OIF-400ZR, Open ROADM, and Open ZR+, is shown in Table 1.
| Standard | OIF-400ZR | Open ROADM | Open ZR+ |
| Target Application | DCI | MAN & Long haul | DCI& MAN |
| Client side | 400GE | 100~400GE
OTN |
100G~400GE |
| Reach | <120km | 120km~500km | 120km~1400km |
| Package | QSFP-DD/OSFP | CFP2 or other | QSFP-DD/OSFP |
| FEC type | CFEC | oFEC | oFEC |
| Power consumption | <15W | Undefine | <20W |
Table 1: Comparison of Interoperability Standard Parameters of 400ZR, Open ROADM and Open ZR+ Coherent Optical Modules
Applications for 400G ZR, Open ROADM and ZR+
As the network data traffic keeps increasing year by year, the coherent light transmission technology has been adopted in more and more application in the field of modern optical communication. The coherent technology has been extended from the backbone network (with a distance of over 1,000 km) to the metro network (with a distance ranging from 100 km to 1,000 km) and even to the edge access network (with a distance of less than 100 km).
On the other hand, in the field of data communication, the coherent technology has also become the mainstream solution for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) (with a distance of 80 – 120 km).
With the support of new standards, 400G coherent optical solutions can offer significant advantages and flexibility, and are expected to provide faster data streams between data centers to meet the ever-growing data demands.
These new standards have greatly increased the bandwidth capacity and reduced the operating costs (with fewer transceivers), decreased the space occupied by equipment and power consumption, which will enable hyperscale data centers, distributed data centers and metro telecom networks to provide the 400G interconnection speed required by emerging technologies.
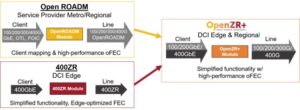
A Look into the Future
From the perspective of standardization evolution, the next-generation ultra-400G coherent pluggable products are very likely to adopt a single-wavelength rate of 800G.
Recently, the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) is discussing and formulating the 800ZR, which is the next-generation coherent technology standard for 400ZR.
Currently, the initially considered goal is to support 80 – 120 km (amplified) DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) links for Data Center Interconnect (DCI) scenarios, and 2 – 10 km unamplified links for campus scenarios.
The client-side interface supports 2 × 400GE or 1 × 800GE, and the line-side supports a single-wavelength 800G coherent line interface. The frame structure indicators mapped from the client side to the line side as well as the line-side signal indicators are defined to achieve interoperability.