An Ultimate Introduction to WDM and CWDM and DWDM
WDM and CWDM and DWDM explained
What is a wavelength?
Light is a kind of electromagnetic wave, and the wavelength refers to the distance between the peak/trough of the electromagnetic wave and the adjacent peak/trough.
What is WDM?
WDM is the abbreviation of Wavelength Division Multiplexing. It refers to a technology that couples optical carrier signals of two or more wavelengths to an optical fiber for transmission through a wavelength division multiplexer (Multiplexer), improving single-wavelength transmission. The transmission bandwidth of the optical fiber.
What are CWDM and DWDM?
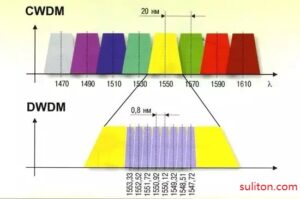
CWDM is the abbreviation of Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. CWDM has a wide wavelength interval, and the industry standard is 20nm.
DWDM is the abbreviation of Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing. The wavelength interval of DWDM is very narrow, and there are several industry standards such as 0.2nm/0.4nm/0.8nm.

CWDM vs DWDM, What Are Their Differences?
CWDM vs DWDM: Channel Spacing
CWDM 20nm DWDM 0.2nm
CWDM vs DWDM: Transmission Distance
The transmission distance of both is the same
CWDM vs DWDM: Modulation Laser
Both modulation types are also the same
CWDM vs DWDM: Bandwidth
The CWDM system accommodates a small number of wavelengths and the system bandwidth is relatively small
The DWDM system can accommodate up to nearly 200 channel wavelengths, and the system bandwidth is very large
CWDM vs DWDM: Application
CWDM vs DWDM: Cost
CWDM has a wide wavelength channel spacing, the manufacturing and control of the laser machine is relatively simple, and the cost is relatively low; DWDM has high requirements for the wavelength and stability of the laser, and the cost is relatively high
CWDM vs DWDM: Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of CWDM: low system cost, no special requirements for single-mode fiber type, laser does not require wavelength control, and system functions are small.
Disadvantages of CWDM: the market size is small and the cost advantage is not obvious enough; there are few wavelength channels used and the system bandwidth is not high enough to meet the needs of the rapidly developing communications market.
Advantages of DWDM: large transmission capacity; saves fiber resources; long transmission distance, can be used with EDFA to achieve hundreds of kilometers of transmission; can form an all-optical network.
Disadvantages of DWDM: high optical device manufacturing precision requirements, difficult wavelength control, and high optical device cost.
Active and passive systems: What’s the difference?
Active devices refer to devices or equipment that require external power supply to work properly. In optical communication systems, such as optical modules, optical amplifiers, and communication hosts are all active devices.
Passive (passive) devices do not have any form of power supply inside. They only need to input signals and can work normally without external power supply. In optical communication systems, such as optical fibers, optical attenuators, and wavelength division multiplexers are all passive device.
Conclusion
In short, CWDM and DWDM have their own characteristics, and users can configure them appropriately according to project budget and needs. In the long run, DWDM is more in line with the needs of future communication development, because it has the advantages of larger transmission capacity and longer transmission distance. If you still have relevant questions, you are welcome to contact us via email.
FAQ
What is CWDM and DWDM’s potential for scalability?
Both CDWM and DWDM have good scalability. CDWM and DWDM systems use ordinary single-mode optical fibers. In the original single-mode optical fiber communication network, the ordinary optical modules are replaced with CWDM or DWDM, and the optical modules are replaced with CWDM or DWDM. The transmitting and receiving ends of the module are combined together through a CWDM or DWDM wavelength division multiplexer respectively, and can be directly connected to the original optical network.
CWDM/DWDM: 10G vs 25G vs 100G solution for long distance traffic
The communication wavelength of DWDM is at 1550nm. The traditional G.652 optical fiber has the lowest loss at 1550nm and has a long transmission distance. It is basically widely used in 10G optical modules. However, due to the influence of G.652 optical fiber at 1550nm dispersion, 25G/100G optical modules Due to the limitation of dispersion, the transmission distance can only support up to 15km, which cannot fully utilize the advantages of large capacity, high bandwidth and long distance of the DWDM system, so it is rarely used.
CWDM is used at both wavelengths of 1310nm and 1550nm. The zero dispersion point of G.652 fiber is near 1310nm, and the dispersion coefficient is extremely low. Therefore, 25G/100G optical modules mostly use CWDM systems.
BiDi Bidirectional Single Fiber CWDM
Usually the CDWM technology standard is used inside the BiDi optical module. Two different wavelengths are used for transmission and reception. The requirements of the wavelength standard and CWDM are consistent.
What is the difference between TDM and WDM?
TDM is the abbreviation of Time Division Multiplexing. It uses the same optical fiber channel and a single optical wavelength, and different channels are divided into different times for transmission.
CWDM is the abbreviation of Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. It uses the same optical fiber channel and multiple optical wavelengths. Each channel occupies one wavelength, and each wavelength directly affects the signal complementation.
OEO as signal regenerator in WDM Network?
OEO is a regeneration technology based on light-electricity-light. After the optical signal is transmitted over long distances, it is affected by the attenuation, dispersion, scattering and some external interference of the optical fiber. The signal is seriously degraded, and the optical signal needs to be improved through regeneration technology. Quality, keep transmitting. OEO refers to converting optical signals into electrical signals first, reshaping and timing the signals on the circuit, and then converting them into optical signals to achieve signal regeneration.
OEO can be used in conjunction with WDM to achieve long-distance, large-capacity signal transmission.
What is the WDM network?
WDM network refers to a transmission network that uses wavelength division multiplexing technology
Why not just add more wavelengths?
Whether it is CWDM or DWDM, the wavelength channels used need to comply with ITU-T standards to prevent direct signal crosstalk between different channels. Under the requirements of the wavelength spacing standard, the number of channels in each band is limited.
Should you use CWDM or DWDM?
The selection of CWDM or DWDM needs to be determined based on the module transmission capacity, single-channel transmission rate, and transmission distance. CDWM generally has only 4 channels or 8 channels, calculated according to the ship speed of a single channel. If it can meet the capacity requirements, you can choose a CWDM system; if it cannot meet the capacity requirements, you need to upgrade to a DWDM system. In addition, if the communication distance exceeds 80km, EDFA needs to be used for relay amplification in the middle. The channel wavelength of CWDM exceeds the working range of EDFA, and DWDM also needs to be selected.
Can CWDM and DWDM be used together in a network?
They cannot be used at the same time. In the 1550nm band, the channel wavelengths of CWDM and DWMD overlap. Using them at the same time will cause serious crosstalk and cause signal interruption.
What is the future of CWDM/DWDM?
With the continuous development of communication technology and the continuous growth of data transmission business volume, CWDM/DWDM has broad application prospects in the future. CWDM is increasingly used in high-speed optical modules, such as 25G/100G/400G optical modules. Due to the influence of dispersion, DWDM has limited application in traditional 25G/100G optical modules. However, on 100G/400G related optical modules, using DWDM and EDFA can achieve large-capacity transmission of hundreds to thousands of kilometers.




One Comment